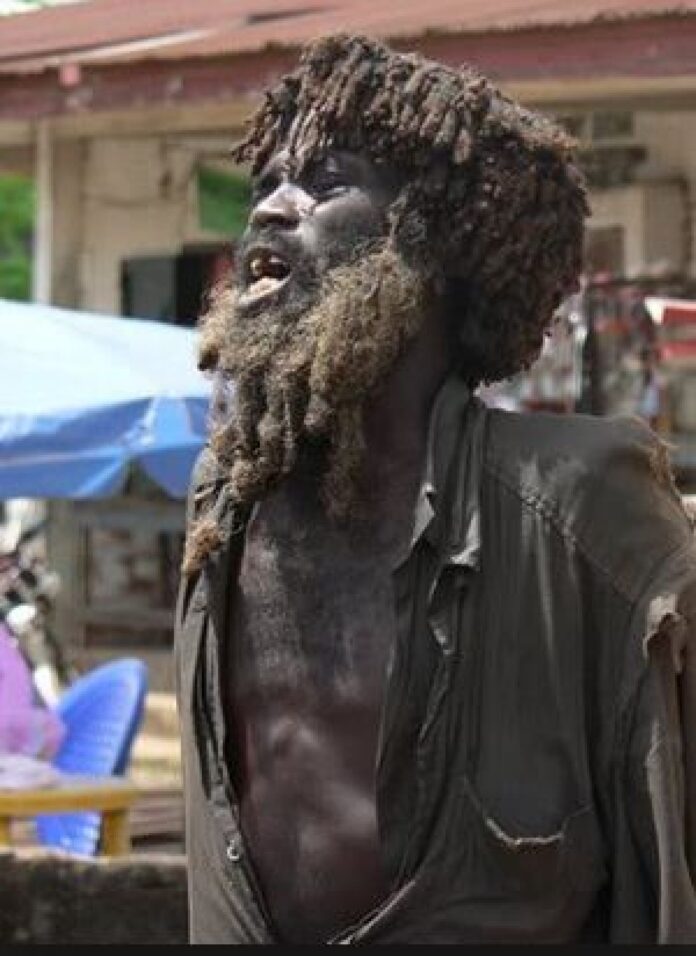
In the bustling streets of Nigeria, where vibrant cultures intertwine and resilient spirits thrive, there exists a silent struggle that often goes unnoticed: the battle against mental health stigma. Behind the colorful façade of festivals and the rhythmic beats of Afrobeat music, lies a pervasive societal stigma that shrouds discussions of mental illness in shame and secrecy. In a country where communal bonds run deep, the reluctance to acknowledge and address mental health challenges persists, leaving countless individuals to suffer in silence. However, amidst this backdrop of stigma, a growing movement is emerging—one fueled by courage, compassion, and a collective determination to shatter the barriers of misconception and silence. This article delves into the multifaceted landscape of mental health stigma in Nigeria, exploring its roots, its impact, and the transformative efforts underway to foster understanding, acceptance, and healing within Nigerian communities. Through the exploration of key variables shaping mental health stigma in Nigeria, this article aims to enlighten readers on several crucial aspects:
1. Cultural Dynamics:
Cultural dynamics play a profound role in shaping attitudes and perceptions surrounding mental health in Nigeria. For instance, traditional beliefs often attribute mental illness to spiritual causes, such as witchcraft or curses, leading to stigmatization and ostracization of affected individuals. In many communities, seeking psychiatric help is viewed as a sign of weakness or moral failing, further perpetuating the stigma.

Moreover, the emphasis on collectivism and communal values in Nigerian society can deter individuals from seeking help for fear of bringing shame upon their families. The concept of “face” or reputation holds significant weight, and disclosing mental health issues may be seen as damaging to one’s social standing.
Religious beliefs also influence attitudes towards mental health. While faith can provide solace and support, there may be a tendency to rely solely on prayer or spiritual interventions, overlooking the importance of professional treatment.
Additionally, gender norms and expectations may exacerbate stigma, particularly for men who are often socialized to suppress emotions and appear strong. Seeking help for mental health concerns may be perceived as emasculating, leading to underreporting and untreated conditions.
By understanding these cultural dynamics, it becomes evident that addressing mental health stigma in Nigeria requires a nuanced approach that respects and engages with diverse belief systems while promoting evidence-based interventions and destigmatizing attitudes towards seeking help.
2. Systemic Challenges:
Systemic challenges pose significant barriers to accessing mental health services in Nigeria, exacerbating the stigma surrounding mental illness. One notable obstacle is the severe shortage of mental health professionals and facilities across the country. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Nigeria has fewer than 200 psychiatrists serving a population of over 200 million people, resulting in an alarming treatment gap.
Geographic disparities further compound the issue, with mental health services predominantly concentrated in urban areas, leaving rural communities underserved. This disparity in access means that many individuals must travel long distances to access care, facing financial burdens and logistical challenges in the process.
Financial constraints also present a formidable barrier to care. Mental health services are often costly, and many Nigerians cannot afford out-of-pocket expenses for consultations, medications, or therapy sessions. Furthermore, mental health coverage under existing health insurance schemes is limited, leaving many uninsured individuals without access to essential treatment.
The lack of integration of mental health into primary healthcare exacerbates the problem. Mental health is often treated as a separate issue rather than being integrated into routine healthcare services, leading to missed opportunities for early intervention and prevention.
These systemic challenges underscore the urgent need for comprehensive healthcare reforms that prioritize mental health, including increased investment in mental health infrastructure, workforce development, and the integration of mental health services into primary care settings. Additionally, policies aimed at improving mental health coverage and reducing financial barriers to care are essential for addressing the pervasive stigma surrounding mental illness in Nigeria.

3. Government Initiatives:
Despite the pervasive challenges, the Nigerian government has undertaken various initiatives to address mental health stigma and improve access to care. One notable effort is the National Mental Health Policy, which was adopted in 1991 and revised in 2013. This policy provides a framework for the delivery of mental health services and emphasizes the integration of mental health into primary healthcare.
Additionally, the government has implemented various programs and campaigns to raise awareness and reduce stigma surrounding mental health. For example, the Federal Ministry of Health, in collaboration with partners, has organized mental health awareness events, such as World Mental Health Day activities and campaigns to challenge misconceptions and promote understanding
Despite these initiatives, challenges persist, and there is a need for sustained commitment and investment to address the complex interplay of factors contributing to mental health stigma in Nigeria. Collaborative efforts involving government, civil society, healthcare professionals, and communities are essential to drive meaningful change and ensure that all Nigerians have access to the support and services they need to achieve mental well-being.
4. Educational Campaigns:
Educational campaigns play a crucial role in challenging mental health stigma and promoting understanding and empathy within Nigerian communities. One such initiative is the “Mental Health Awareness Campaign,” launched by organizations such as the Mental Health Foundation Nigeria and the Association of Psychiatrists in Nigeria. These campaigns utilize various platforms, including social media, community events, and school outreach programs, to disseminate accurate information about mental health and combat misconceptions.
Another example is the “Mind Matters Initiative,” which focuses on promoting mental health literacy among youth and young adults in Nigeria. Through workshops, seminars, and peer-led initiatives, this campaign empowers individuals to recognize the signs of mental distress, seek help when needed, and support peers experiencing mental health challenges.
Additionally, educational institutions play a crucial role in raising awareness about mental health. Some universities in Nigeria have implemented mental health education programs and counseling services to support students’ emotional well-being. These initiatives aim to reduce stigma on campus, provide resources for students in distress, and foster a supportive environment for mental health.
Furthermore, media partnerships have been instrumental in amplifying educational messages about mental health. Television programs, radio broadcasts, and online platforms have featured discussions, documentaries, and storytelling initiatives to raise awareness, challenge stereotypes, and promote positive representations of mental health.
By engaging diverse audiences through educational campaigns, Nigeria is making strides in breaking down the barriers of stigma and fostering a culture of empathy, acceptance, and support for individuals living with mental illness. However, sustained efforts are needed to ensure that mental health education remains a priority and reaches all segments of Nigerian society.

5. Media Influence:
The media holds significant influence in shaping public perceptions and attitudes towards mental health in Nigeria. Unfortunately, misrepresentation and sensationalism often exacerbate stigma and perpetuate harmful stereotypes. However, there are also instances where the media has been instrumental in challenging stigma and promoting positive narratives surrounding mental health.
One common misrepresentation in Nigerian media is the portrayal of individuals with mental illness as dangerous or unpredictable. Sensationalized depictions in movies, television shows, and news reports often reinforce negative stereotypes, contributing to fear and misunderstanding among the public.
Moreover, mental health issues are frequently stigmatized and trivialized in Nigerian media, with derogatory language and insensitive jokes further marginalizing individuals living with mental illness. Such portrayals not only perpetuate stigma but also discourage individuals from seeking help due to fear of judgment or discrimination.
However, there are examples of media initiatives that strive to counteract stigma and promote accurate representations of mental health. For instance, some Nigerian journalists and media outlets have produced investigative reports and documentaries that shed light on the challenges faced by individuals living with mental illness and advocate for improved access to care.
Additionally, social media platforms have emerged as powerful tools for raising awareness and challenging stigma surrounding mental health. Influencers, celebrities, and advocacy groups use their online platforms to share personal stories, provide resources, and promote messages of hope and resilience, reaching diverse audiences across Nigeria.
By holding the media accountable for responsible reporting and amplifying voices that advocate for mental health awareness and acceptance, Nigeria can harness the power of storytelling to drive positive change and foster a more inclusive and empathetic society.
6. Community Support:
Community support plays a pivotal role in addressing mental health stigma and providing crucial assistance to individuals living with mental illness in Nigeria. One example of community support is the establishment of support groups and peer-led initiatives. These groups provide safe spaces for individuals to share their experiences, receive validation, and access peer support from others who understand their struggles. Organizations like the Mental Health Support Initiative and Mentally Aware Nigeria Initiative (MANI) facilitate support groups and online forums where individuals can connect and find solidarity.
Furthermore, traditional and religious leaders often play a significant role in providing community support for mental health. In many Nigerian communities, these leaders are respected figures who wield influence and can help challenge stigma and promote understanding. Some religious organizations have established counseling services and prayer groups to support individuals experiencing mental health challenges, providing spiritual and emotional guidance.
Moreover, family and community networks serve as lifelines for individuals living with mental illness. While stigma may exist within families, many families offer unconditional love and support to their loved ones. Family members often play caregiving roles, providing practical assistance and emotional support to individuals with mental health conditions.
Volunteer-driven initiatives also contribute to community support efforts. For example, the “Yellow Heart Initiative” mobilizes volunteers to provide mental health education, support, and referrals in local communities. These grassroots efforts raise awareness, reduce stigma, and connect individuals with resources and services.
By harnessing the power of community support, Nigeria can create a network of care and solidarity that empowers individuals living with mental illness and fosters a culture of acceptance and inclusion. Collaboration between communities, government agencies, and civil society organizations is essential to strengthen community support systems and ensure that no one faces mental health challenges alone.
7. Intersectional Perspectives:
Intersectional perspectives are crucial in understanding how various social identities intersect and shape experiences of mental health stigma in Nigeria. For instance, women in Nigeria may face unique challenges due to the intersection of gender and mental health. Cultural norms and gender roles may dictate that women prioritize caregiving responsibilities and suppress their own mental health needs, leading to underreporting and untreated conditions.
Additionally, women may face higher rates of stigma and discrimination, particularly regarding reproductive health and maternal mental health issues.
Moreover, socioeconomic factors intersect with mental health stigma, exacerbating disparities in access to care. Individuals living in poverty may face additional barriers to accessing mental health services, such as limited financial resources, lack of transportation, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure in their communities. The stigma associated with poverty and mental illness further compounds the challenges faced by these individuals, perpetuating cycles of marginalization and exclusion.
Rural communities in Nigeria also experience unique intersectional challenges in accessing mental health care. Limited access to healthcare facilities, shortage of mental health professionals, and cultural beliefs may intersect to create significant barriers to seeking help for mental health issues.
Additionally, individuals living in rural areas may face social isolation and lack of community support, further impacting their mental well-being.
By recognizing and addressing these intersectional perspectives, Nigeria can develop more inclusive and equitable approaches to mental health care that consider the diverse needs and experiences of its population. Efforts to reduce stigma must be intersectional, taking into account the complex interplay of factors such as gender, sexuality, socioeconomic status, and geographic location. Only through inclusive strategies can Nigeria create a society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive mentally and emotionally.

In conclusion, the journey to address mental health stigma in Nigeria is multifaceted, marked by both challenges and inspiring progress. From cultural beliefs and systemic barriers to community support and intersectional perspectives, the landscape of mental health stigma reflects the complexities of Nigerian society. Yet, amidst these challenges, there are glimmers of hope—government initiatives, educational campaigns, media influence, and grassroots efforts—that signal a transformative shift towards greater awareness, acceptance, and support for mental health.
As we navigate the path forward, let us remember that mental health knows no bounds—it affects individuals of all backgrounds, regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic status. By fostering empathy, understanding, and solidarity, Nigeria can pave the way for a future where mental health is viewed not as a source of shame, but as a fundamental aspect of human well-being deserving of compassion and care.
Together, let us continue to challenge stigma, advocate for inclusive policies, and build resilient communities that prioritize mental health. In doing so, we not only honor the dignity and worth of every individual but also lay the foundation for a brighter, more compassionate future for Nigeria and its people.