The International Telecommunications Union (ITU) has released its Global Cybersecurity Index 2024, ranking Nigeria as a tier-3 country. This ranking indicates that Nigeria has made some progress in cybersecurity but still needs improvement.
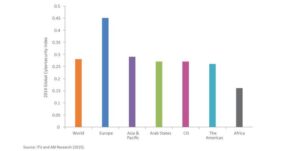
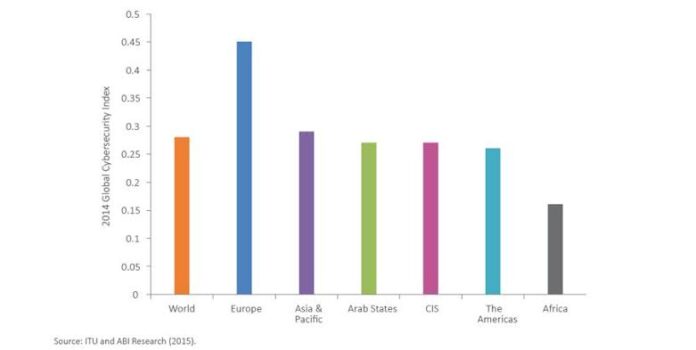
The ITU assessed 194 countries across five pillars: legal, technical, organizational, capacity development, and cooperation. Nigeria scored highest in legal measures, with 19.52 out of 20 marks. This is likely due to the country’s Cybercrime Act 2015, which was amended in 2024.
The ITU report categorizes countries into five tiers based on their cybersecurity efforts. Tier-1 and tier-2 countries demonstrate strong commitment to cybersecurity, while tier-3 and tier-4 countries are improving but still have work to do. Tier-5 countries lag behind in all five pillars.
Nigeria’s ranking as a tier-3 country means it has some cybersecurity measures in place but needs to strengthen them. The report highlights the importance of building trust in the digital world and encourages countries to focus on cybersecurity to ensure safe and secure management of cyber threats.
The ITU report also notes that the African region has made significant progress in cybersecurity since 2021, with many countries implementing essential legal measures, plans, and capacity-building initiatives. However, some countries still face resource and capacity constraints in their cybersecurity efforts.
The report warns of increasing cyber threats, including ransomware attacks, cyber breaches, and data breaches. In 2023, over 2,800 reported breaches resulted in 8 billion records being compromised, with the average cost of a data breach increasing by 15% over the past three years.
To address these threats, countries are implementing regulations on personal data protection, privacy protection, and breach notification. The ITU encourages countries to continue improving their cybersecurity efforts to ensure a safe and secure digital world.